Morvarid Mohammadian Bajgiran, a recent graduate with a Master’s in engineering from Concordia University, Montreal, has recently published the following article in the International Journal of Applied Ceramic Technology
Morvarid Mohammadian Bajgiran | Milad Rezvani Rad | Andre McDonald |
Christian Moreau
In coating-based resistive heating systems applied on an electrically conductive substrate, an intermediary dielectric layer is required to minimize or eliminate leakage of current from the heating surface to the substrate. Aluminum oxide has widely been used for electrical insulation purposes.
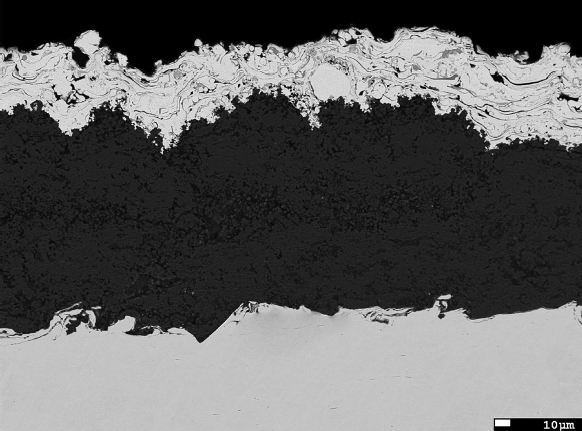
In this study, alumina was deposited onto carbon steel substrates by using suspension plasma spraying and flame spraying processes. Then, Ni-20Cr, as the heating element, was deposited on the alumina layer by using air plasma spraying.
The resultant microstructure and phase composition of the alumina layers were evaluated by using scanning electron microscope images, X-ray diffraction analysis, and Raman spectroscopy.
The breakdown voltage of alumina layers was measured independently and within the heating system. It was found that the dielectric properties of alumina layers were significantly affected by its microstructural features. It was observed that penetration of metal topcoat into the alumina layer decreased the overall breakdown voltage of the system.